Set Up Crons
Sentry Crons allows you to monitor the uptime and performance of any scheduled, recurring job in your application.
Once implemented, it'll allow you to get alerts and metrics to help you solve errors, detect timeouts, and prevent disruptions to your service.
- Use our getting started guide to install and configure the Sentry Python SDK (min v1.17.0) for your recurring job.
- Create and configure your first Monitor.
If you're using Celery Beat to run your periodic tasks, have a look at our Celery Beat Auto Discovery documentation.
Use the Python SDK to monitor and notify you if your periodic task is missed (or doesn't start when expected), if it fails due to a problem in the runtime (such as an error), or if it fails by exceeding its maximum runtime.
Use the monitor decorator to wrap your tasks:
import sentry_sdk
from sentry_sdk.crons import monitor
# Add the @monitor decorator to your task
@monitor(monitor_slug='<monitor-slug>')
def tell_the_world():
print('My scheduled task...')
Alternatively, monitor can be used as a context manager:
import sentry_sdk
from sentry_sdk.crons import monitor
def tell_the_world():
with monitor(monitor_slug='<monitor-slug>'):
print('My scheduled task...')
Since version 1.44.1 of the SDK you can use monitor to annotate asynchronous functions as well.
You can create and update your monitors programmatically with code rather than creating and configuring them in Sentry.io. If the monitor doesn't exist in Sentry yet, it will be created.
To create or update a monitor, use monitor as outlined above and pass in your monitor configuration as monitor_config. This requires SDK version 1.45.0 or higher.
# All keys except `schedule` are optional
monitor_config = {
"schedule": {"type": "crontab", "value": "0 0 * * *"},
"timezone": "Europe/Vienna",
# If an expected check-in doesn't come in `checkin_margin`
# minutes, it'll be considered missed
"checkin_margin": 10,
# The check-in is allowed to run for `max_runtime` minutes
# before it's considered failed
"max_runtime": 10,
# It'll take `failure_issue_threshold` consecutive failed
# check-ins to create an issue
"failure_issue_threshold": 5,
# It'll take `recovery_threshold` OK check-ins to resolve
# an issue
"recovery_threshold": 5,
}
@monitor(monitor_slug='<monitor-slug>', monitor_config=monitor_config)
def tell_the_world():
print('My scheduled task...')
If you're using manual check-ins, you can pass your monitor_config to the capture_checkin call:
check_in_id = capture_checkin(
monitor_slug='<monitor-slug>',
status=MonitorStatus.IN_PROGRESS,
monitor_config=monitor_config,
)
Check-in monitoring allows you to track a job's progress by capturing two check-ins: one at the start of your job and another at the end of your job. This two-step process allows Sentry to notify you if your job didn't start when expected (missed) or if it exceeded its maximum runtime (failed).
If you use the monitor decorator/context manager, the SDK will create check-ins for the wrapped code automatically.
from sentry_sdk.crons import capture_checkin
from sentry_sdk.crons.consts import MonitorStatus
check_in_id = capture_checkin(
monitor_slug='<monitor-slug>',
status=MonitorStatus.IN_PROGRESS,
)
# Execute your task here...
capture_checkin(
monitor_slug='<monitor-slug>',
check_in_id=check_in_id,
status=MonitorStatus.OK,
)
When your recurring job fails to check in (missed), runs beyond its configured maximum runtime (failed), or manually reports a failure, Sentry will create an error event with a tag to your monitor.
To receive alerts about these events:
- Navigate to Alerts in the sidebar.
- Create a new alert and select "Issues" under "Errors" as the alert type.
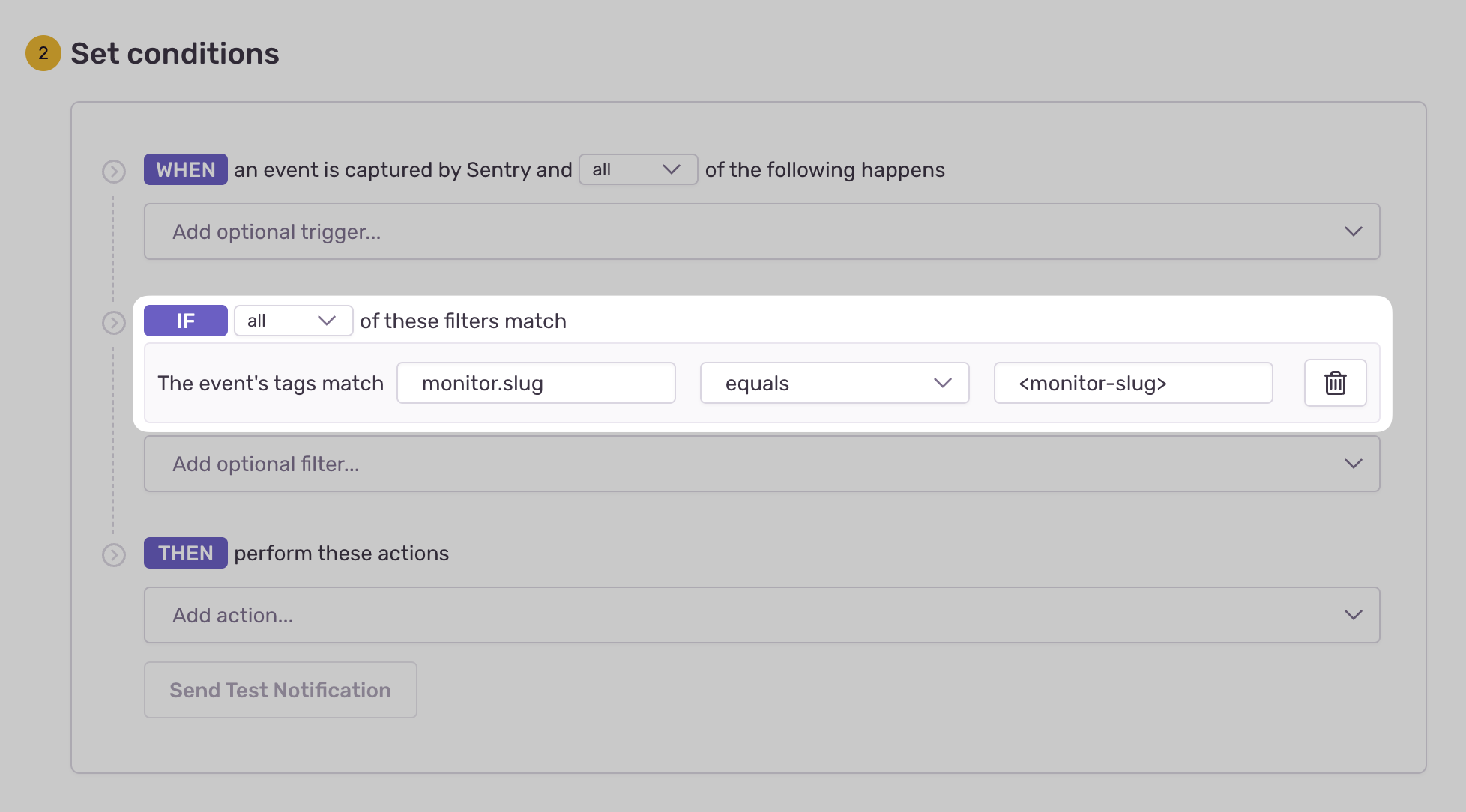
- Configure your alert and define a filter match to use:
The event's tags match {key} {match} {value}.
Example: The event's tags match monitor.slug equals my-monitor-slug-here
Learn more in Issue Alert Configuration.
Crons imposes a rate limit on check-ins to prevent abuse and resource overuse. Specifically, you can only send a maximum of 6 check-ins per minute per existing monitor environment. This limit is enforced on a per-project basis, meaning that the rate limit applies collectively to all monitor environments within a given project. You can check if any of your check-ins are being dropped in the Usage Stats page.
To avoid dropped check-ins, it is crucial to manage and distribute your check-ins efficiently within the rate limits. This will help maintain accurate monitoring and ensure that all critical check-ins are captured and processed.
Our documentation is open source and available on GitHub. Your contributions are welcome, whether fixing a typo (drat!) or suggesting an update ("yeah, this would be better").